Without Securing Talent, Korea Has No Future
• Publication date 2026-01-01
• Hit 1114

Technological hegemony surrounding artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a central facet to national economies and security. Global competition among countries and corporations to secure high-level talent has intensified into a matter of survival. Worldwide demand for AI talent now exceeds supply by more than threefold. In Silicon Valley, AI dominates discussion, and competition among big tech firms to attract talent is escalating. Ultimately, the rivalry between the United States and China will be decided not only by capital or technology but by who succeeds in attracting and retaining global talent.

In South Korea, concerns over talent outflows from Korea are growing. Last year, Korea ranked fourth among the 38 OECD countries in terms of AI talent outflow. Compared to other advanced economies, Korea’s AI industrial ecosystem remains underdeveloped, while overseas firms offer better compensation and research environments. The recent phenomenon of 56 Seoul National University professors relocating abroad over the past four years, a “new brain drain,” must be understood in this broader structural context.
This reality is also clearly reflected in the Global Talent Competitiveness Index, published annually by INSEAD. Korea ranked 31st this year, a position disproportionately low relative to its economic standing, and fell seven places compared to two years ago. In particular, Korea performed poorly in attracting and retaining talent, ranking 55th and 37th, respectively. These findings suggest that beyond economic incentives, social, cultural, and environmental factors play a decisive role in talent mobility.
Korea’s talent outflow is especially alarming because it coincides with record-low fertility rates and rapid population aging. Before this convergence hardens into irreversible decline, Korea must establish a Ministry of Human Resources to oversee a comprehensive national talent strategy and devise systemic measures for talent development, attraction, and utilization.
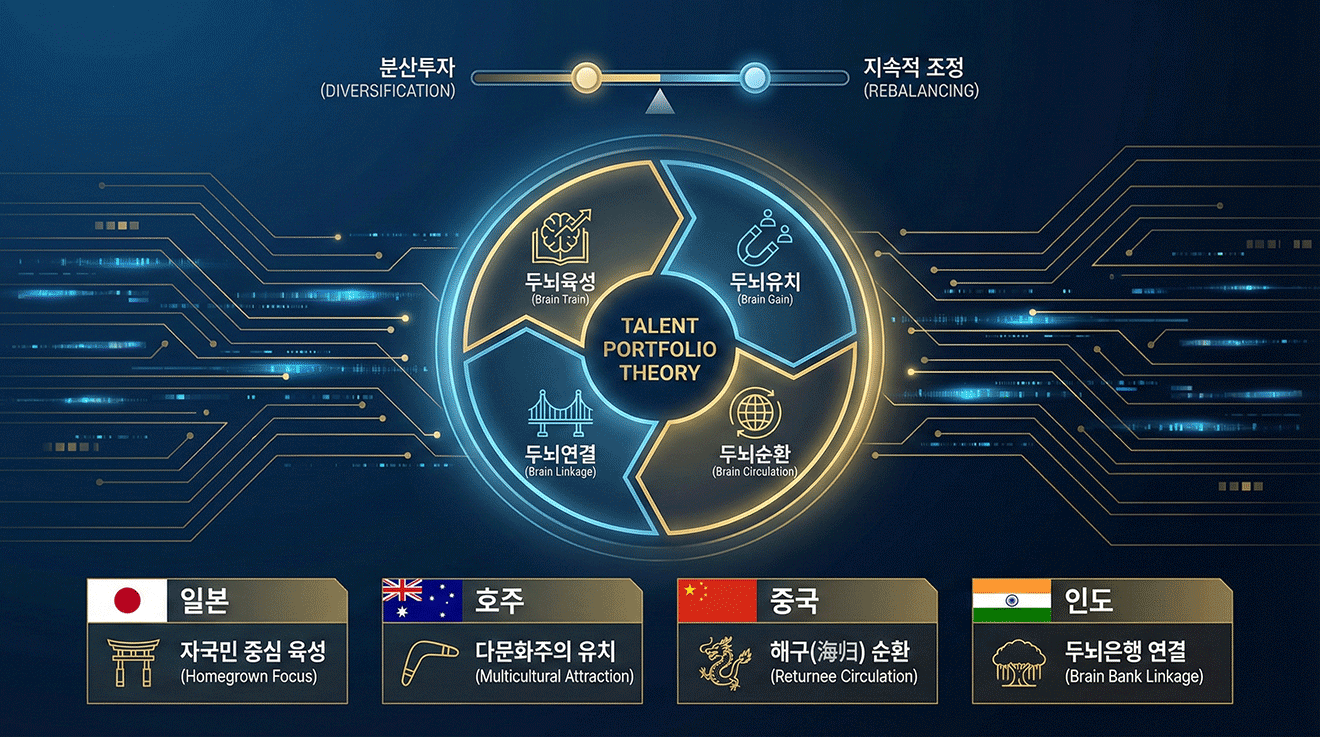
Talent Portfolio Theory
In a recent book published by Stanford University Press, The Four Talent Giants, I proposed “talent portfolio theory.” Just as financial investment strategies adopt a portfolio approach, national talent strategies should also be portfolio-based, emphasizing diversification to minimize risk and continuous adjustment (rebalancing). In other words, just as financial portfolios are composed of cash, stocks, real estate, and bonds, talent portfolios consist of four elements—the “4Bs”: brain train, brain gain, brain circulation, and brain linkage.
Moreover, just as investors design different portfolios, each country’s talent portfolio varies depending on its economic needs as well as cultural and institutional contexts. Japan, Australia, China, and India (all discussed in the book) include all four Bs but have constructed distinct portfolios that contributed to their respective economic development. A portfolio approach transcends the traditional binary of “brain drain versus brain gain” and offers a more comprehensive and flexible framework for understanding national talent strategy, one that is particularly relevant for Korea.
First, “brain train” refers to developing domestic human resources through education and training. It is a fundamental element of any portfolio. In Japan’s portfolio in particular, homegrown talent accounts for a large share. Japan has favored domestically educated and trained talent over foreign or overseas-trained individuals, making them the backbone of its economic development.
By contrast, Australia places greater emphasis on “brain gain.” Brain gain involves importing foreign labor, and approximately 30 percent of Australia’s workforce is foreign-born. Until the 1970s, Australia upheld the “White Australia” policy, but a major shift toward multiculturalism subsequently elevated brain gain to a central position in its portfolio. Brain gain pathways include the study-to-work route, where international students remain for employment, and the work-to-migration route, where individuals enter on work visas and later settle. Australia has effectively utilized both pathways.
“Brain circulation” involves bringing back nationals who were educated or employed abroad, and it has been critical to China’s portfolio. Following China’s opening in the 1980s, Chinese nationals came to represent the largest share of participants in the global talent market, including international students. Approximately 80 percent of them returned to China after the 2000s. Known as haigui (sea turtles), these returnees played prominent roles in China’s science, technology, education, and economy, supported by numerous central and local government programs designed to promote talent circulation.
“Brain linkage” refers to those who do not return home after studying or working abroad but instead serve as bridges between their host countries and their homeland. By leveraging their local networks, social capital, they support their home country from abroad, making this a key component of India’s portfolio. India refers to them as a “brain bank” or “brain deposit,” exemplified by leaders of Silicon Valley big tech firms such as Google CEO Sundar Pichai.
However, all talent portfolios carry inherent risks. When adjustment is delayed or fails, risks can escalate into crises with negative effects on the broader economy. The experiences of the four countries illustrate this point.
Japan has faced two major risks. A talent strategy centered on domestic talent weakened its global competitiveness, while demographic decline reduced its labor pool. Although Japan actively attracted foreign students to increase brain gain, its exclusive social and cultural environment limited their integration into the workforce after graduation. While there are many reasons behind Japan’s “lost 30 years” since the 1990s, one factor was its failure to adjust a portfolio overly concentrated on domestic talent in a timely manner.
Australia has confronted rising anti-immigration sentiment and tensions with China. Public concern grew over excessive immigration and perceived threats to national identity, prompting the government to tighten immigration policies. Amid conflict with China, Australia diversified its foreign talent sources from China to India and Southeast Asia. The pandemic, which restricted cross-border mobility, dealt a severe blow to Australia’s talent attraction efforts.
In China’s case, despite aggressive brain circulation policies, top-tier global talent has remained hesitant to return, as relinquishing careers built abroad is not easy. China accordingly shifted its focus toward brain linkage for these elite individuals. At the same time, brain circulation and linkage strategies became a source of friction with the United States, and rising anti-immigration and anti-China sentiment in the U.S. and Europe reduced opportunities for study and employment abroad. Recently, China has adjusted its portfolio to strengthen domestic talent development.
India, despite its strong brain linkage, remains vulnerable to brain drain. However, as economic opportunities expand domestically, return migration has increased, gradually reshaping its portfolio composition.
What Should Korea’s Talent Portfolio Strategy Be?
What, then, about Korea? Let us examine Korea’s situation by comparing it with the four countries through the lens of talent portfolio theory.
Brain train: Human resources have been critical to Korea’s economic development, with the government playing a central role. Key examples include preferential policies for technical and commercial high schools during the 1970s under the Park Chung Hee administration to support industrialization, and efforts to internationalize universities in the 1990s as part of globalization. While less dominant than in Japan, brain train has constituted a significant share of Korea’s talent portfolio.
Brain gain: Korea has imported low- and semi-skilled labor from China and Southeast Asia to fill so-called 3D jobs, but attraction of global high-level talent has remained limited. As in Japan, social exclusivity and cultural barriers continue to impede integration.
Brain circulation: Comparable to China, brain circulation has played a vital role in Korea’s economic development. Overseas education and experience have carried strong premiums, and China explicitly benchmarked Korea and Taiwan when designing its own policies.
Brain linkage: Compared to brain circulation, brain linkage has, until recently, occupied a relatively small share of Korea’s portfolio.
Facing the AI era, low fertility, and the crisis of a new brain drain, what strategy should Korea pursue in the global competition for talent? As noted above, rather than fragmented and ad hoc measures, Korea must comprehensively review and continuously adjust its talent strategy through a portfolio approach.
Brain train: Korea must cultivate talent for future industries, particularly in science and engineering. Training should be aligned with AI-related fields to better match university output with corporate demand. The excessive concentration of top students in medical schools must be corrected. Support mechanisms to retain domestic talent should be strengthened. A recent Bank of Korea survey of 1,916 science and engineering master’s and doctoral degree holders working domestically found that 42.9 percent of science and engineering master’s and doctoral graduates are considering overseas employment within three years—an alarming signal. While brain train will remain vital, its relative share is likely to decline.
Brain gain: As demographic crises intensify and the share of brain train diminishes, the necessity and importance of brain gain will grow. In particular, Korea must actively utilize the more than 300,000 foreign students currently in the country as human and social capital. At present, universities focus merely on filling enrollment quotas, and most foreign students either leave Korea immediately after graduation or remain employed only briefly. This, too, constitutes a form of brain drain. To increase the share of brain gain in the portfolio, foreign students must be managed holistically from selection to graduation and employment. While immigration is ultimately inevitable, it must be approached cautiously and deliberately, considering its impact on the domestic labor market and anti-immigration sentiment. Australia’s successful experience offers useful lessons.
Brain circulation: Although it occupies a relatively modest share of Korea’s portfolio, a certain level should be maintained. With declining numbers of students studying abroad and reduced inclination among overseas Koreans to return, care must be taken to prevent a sharp drop in this component. Otherwise, Korea risks losing global competitiveness, as Japan’s experience warns.
Brain linkage: Alongside brain gain, brain linkage is crucial to Korea’s portfolio adjustment. Key target groups include departing domestic talent (the new brain drain), foreign students, and the diaspora. Although their likelihood of reemployment in Korea is low, their potential for exchange and collaboration with Korea remains open. Like India, Korea should foster and support brain linkage by treating them as a “brain bank” or “brain deposit.”

Toward the Establishment of a Ministry of Human Resources
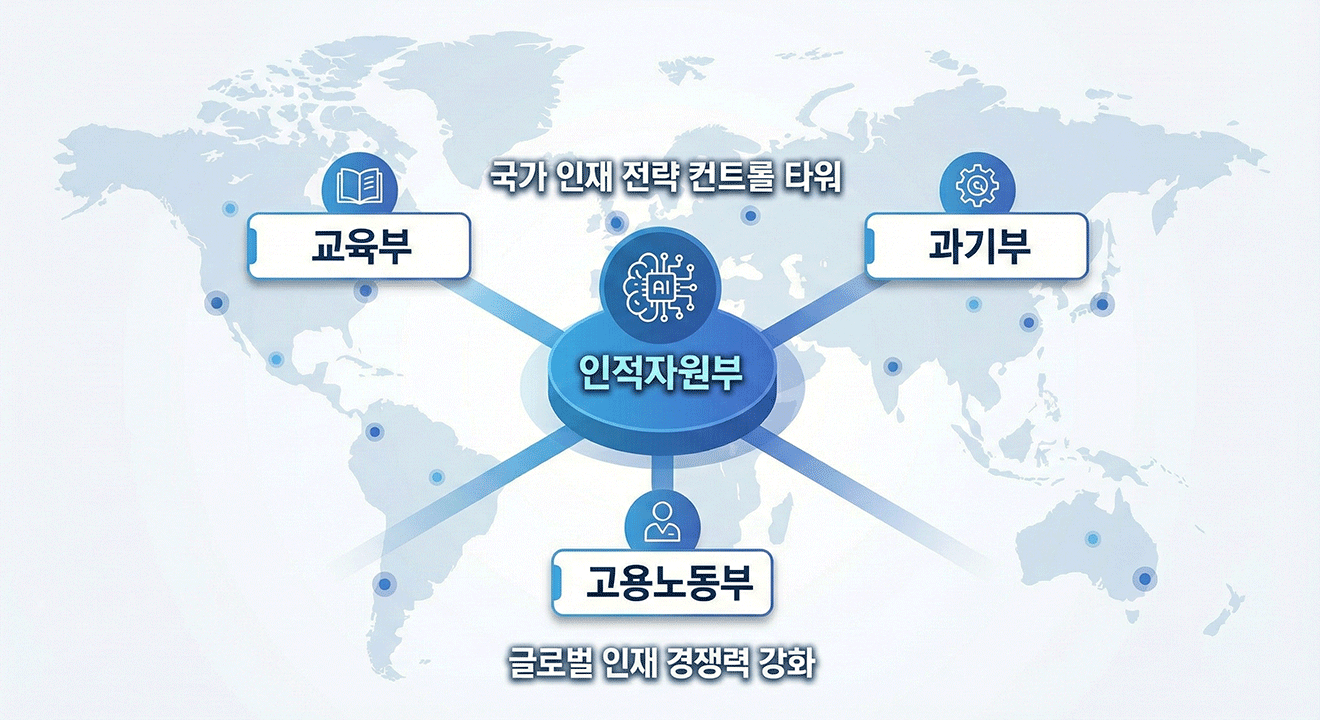
At the national level, a control tower is needed to design an optimal talent portfolio and make timely adjustments. Korea should establish a Ministry of Human Resources by consolidating functions currently dispersed across the Ministry of Education (universities and graduate schools), the Ministry of Science and ICT (R&D), and the Ministry of Employment and Labor (foreign employment support).
It is worth recalling that Singapore, ranked first globally in talent competitiveness, established its Ministry of Manpower early on. Expanded and reorganized from the Ministry of Labor in 1998, it played a pivotal role in transforming Singapore into a talent powerhouse. Through education and development investments, Singapore strengthened domestic talent competitiveness while opening its doors to multinational talent, and it also implemented policies to promote talent circulation and linkage.
From the perspective of talent portfolio theory, Singapore represents a successful case of diversification and continuous adjustment. In the increasingly fierce global competition for talent in the AI era, nations and firms that fall behind cannot secure their future. Korea is no exception.